Recently, results of the phase 2 study of HLX22, an innovative anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody (mAb), in combination with HANQUYOU (HLX02, trastuzumab, trade name: HERCESSI™️ in the U.S., Zercepac® in Europe) and chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric/gastroesophageal junction (G/GEJ) cancer were presented on 2024 ESMO Gastrointestinal Cancers Congress (ESMO GI) and MED, a flagship clinical and translational research monthly journal by Cell Press. The leading principal investigator for this study is Professor Jin Li from Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University. The results showed that the addition of HLX22 to HLX02 (trastuzumab) plus chemotherapy as first-line therapy improved efficacy in HER2-positive G/GEJ cancer patients with manageable safety.
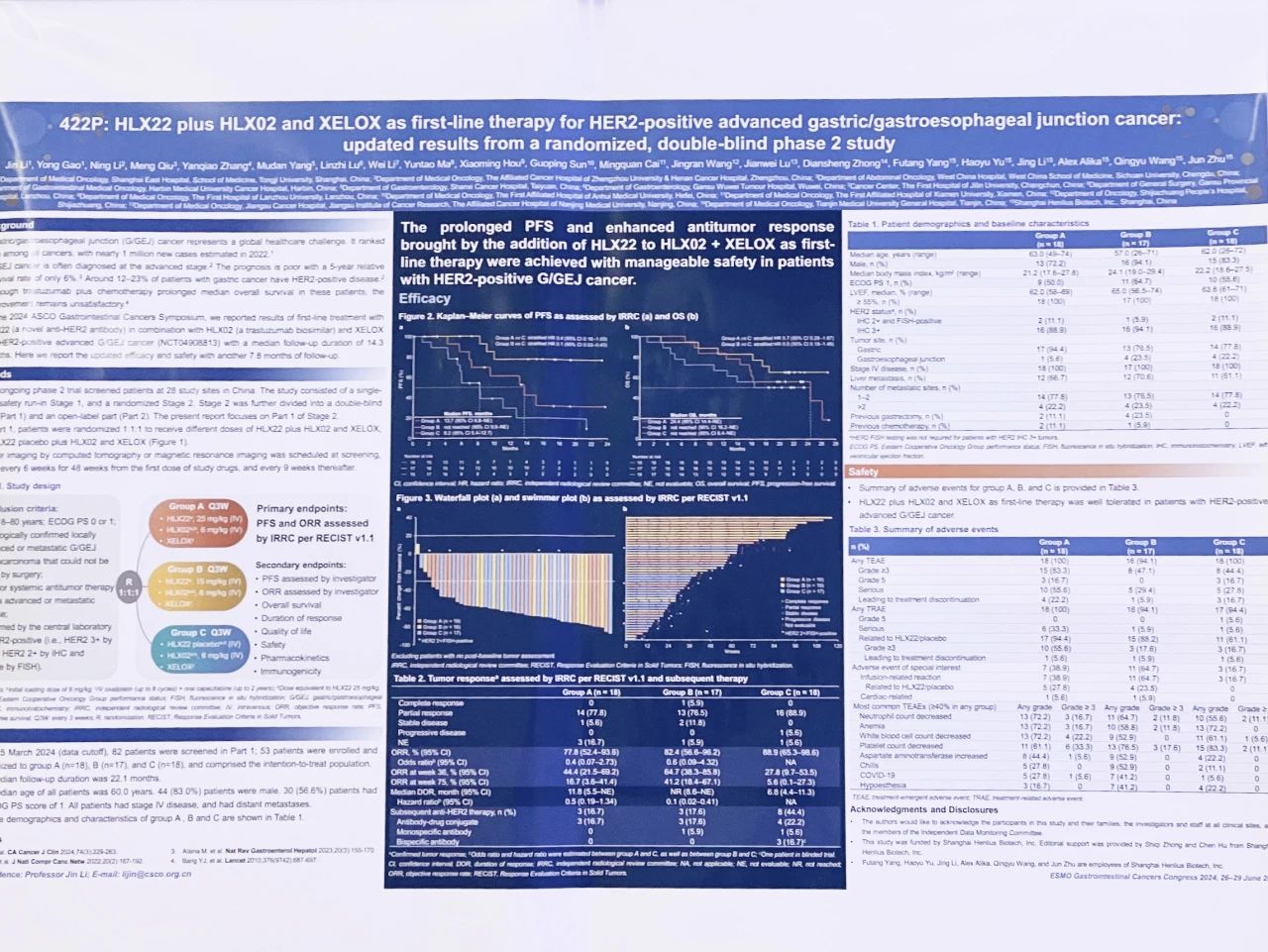
The results of HLX22-GC-201 were first presented at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium (ASCO GI). The study data and updated results with another 7.8 months of follow-up were accepted for publication on MED and for presentation at the 2024 ESCO GI, respectively, which validated the reliability of the results of the study repeatedly and further enhanced the impact of the study in the academic community.
Until now, G/GEJ cancer still constitutes a major global health problem. Globally, there were around 1 million new cases in 2022 [1]. G/GEJ cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage, with a poor prognosis and a 5-year relative survival rate of only 6% [2,3]. The reported rates of HER2 positivity in patients with gastric cancer range from 12% to 23%, and the prognosis for patients with HER2-positive disease used to be even worse than those with HER2-negative disease [2-4]. Currently, for patients with HER2-positive locally advanced/metastatic G/GEJ cancer, the standard first-line treatment is trastuzumab plus chemotherapy. Immunotherapies are recommended to be added for tumours with positive PD-L1 expression defined by combined positive score greater than 1. However, the sustained efficacy and prognosis for these treatments need to be further improved [5], indicating a significant unmet medical need. To date, no dual HER2 blockade therapy for the treatment of HER2-positive gastric cancer has been approved.
HLX22 is an innovative anti-HER2 mAb that was introduced from AbClon, Inc. and further investigated and developed by Henlius. HLX22 can bind to HER2 subdomain IV at a different binding site from trastuzumab, which allows the simultaneous binding of HLX22 and trastuzumab to HER2. Pre-clinical studies showed that the combination therapy of HLX22 and trastuzumab inhibited the cell proliferation induced by epidermal growth factor (EGF) and Histidine-Rich Glycoprotein 1 (HRG1) and enhanced the antitumour activity in vitro and in vivo. The phase 1 clinical trial of HLX22 demonstrates that HLX22 was well tolerated and had good safety profiles [6].
HLX22-GC-201 is a two-stage study aims to compare the efficacy and safety of HLX22 versus placebo in combination with trastuzumab injection (HLX02) and XELOX, as first-line therapy for HER2-positive locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer patients. Stage 1 was a safety run-in stage while stage 2 was a randomised, double-blind, multi-centre, phase 2 study. Stage 2 was further divided into two parts. In part 1, eligible patients were randomised 1:1:1 to receive HLX22 (group A: HLX22, 25mg/kg; group B: HLX22, 15mg/kg) in combination with HLX02 and XELOX, or placebo in combination with HLX02 and XELOX (group C). The primary endpoints include progression-free survival (PFS) and objective response rate (ORR) assessed by independent radiological review committee (IRRC) per RECIST v1.1. The secondary objectives are to evaluate other efficacy endpoints, safety and tolerability.
As of March 25, 2024 (updated data cutoff date), 53 patients were enrolled and randomised to group A (n=18), group B (n=17), and group C (n=18) with a median follow-up duration of 22.1 months. Of the 53 enrolled patients, 44 (83.0%) were male; the median age of all patients was 60.0 years. 30 (56.6%) patients had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) score of 1. Compared with group C (placebo group), the IRRC-assessed median PFS was markedly prolonged (13.7 vs. 8.2 months; stratified HR 0.40, 95% CI 0.16-1.03) in group A; not reached in group B (stratified HR 0.10, 95% CI 0.03–0.43). ORRs were 77.8% vs 82.4% vs 88.9% in A, B and C, respectively. Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were observed in 18 (100.0%), 16 (94.1%), and 17 (94.4%) patients in group A, B, and C, among whom 6 (33.3%), 1 (5.9%), and 1 (5.6%) patients experienced serious TRAEs. Only one (5.6%) patient in group C reported a grade 5 TRAE. HLX22 plus HLX02 and XELOX as first-line therapy was well tolerated in patients with HER2-positive advanced G/GEJ cancer.
Recently, the investigational new drug application (IND) for phase 3 international multicenter clinical study of HLX22 in combination with trastuzumab and chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer has been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Moving forward, Henlius will actively improve efficiency through innovations, with a particular focus on addressing the unmet medical needs, and efficiently promote the clinical development of HLX22 globally, so as to provide more high-quality and affordable therapies for patients worldwide.
【Reference】
[1] Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024: 1-35.
[2] Ajani JA. et al. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2022;20(2):167-92.
[3] Alsina M. et al. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2023;20(3):155-70.
[4] Gravalos C. et al. Ann Oncol 2008;19(9):1523-9.
[5] NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Gastric Cancer V.1.2024
[6] Zhu X, Ding Y, Wang Q, Yang G, Zhou L, Wang Q. HLX22, an anti-HER-2 monoclonal antibody, in patients with advanced solid tumors overexpressing human epidermal growth factor receptor 2: an open-label, dose-escalation, phase 1 trial. Invest New Drugs. 2023;41(3):473-482. doi:10.1007/s10637-023-01338-7
