Recently, results of the phase 2 stage of ASTRUM-015, a phase 2/3 international multi-centre study led by Professor Rui-Hua Xu from Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center and State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, has been published in MED (impact factor: 17), a flagship clinical and translational research monthly journal by Cell Press. The results have shown that serplulimab plus HLX04 (bevacizumab, trade name in China: HANBEITAI) and chemotherapy exhibits promising efficacy and is safe and tolerable in patients with treatment-naïve metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC).
ASTRUM-015 trial is a phase 2/3 study of HANSIZHUANG (serplulimab), an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) developed by Henlius independently, plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with mCRC. The results of the phase 2 stage of ASTRUM-015 were first presented at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium (ASCO GI). Updated results were released online and presented in the poster sessions at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting. This recent publication in a well-recognised international journal further demonstrated the global recognition of serplulimab by the community. Based on these results, the phase 3 part of ASTRUM-015 has been initiated, and the first patient was recently dosed.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignant cancers globally. CRC often spreads before the initial tumour is detected and 95% of CRC cases are of the proficient mismatch repair (pMMR)/ microsatellite stable (MSS) type[1,2]. The advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors has brought new hope for patients with mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR)/microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) metastatic CRC (mCRC) and several PD-1 inhibitors were shown to confer significant survival benefits [3,4]. However, pMMR/MSS mCRC, the predominant type of mCRC, are considered “immune-cold tumours” that are characterised by a low response rate to immunotherapy. To date, there has been no globally approved immunotherapy for the first-line treatment of pMMR/MSS mCRC, indicating a significant unmet medical need for this patient population.
The company is continuing to explore immuno-oncology therapy for mCRC, with the goal of delivering highly effective treatment for a broad population of patients. Between July 16, 2021 and January 20, 2022, 114 patients were enrolled and 112 patients received at least one dose of treatment in the phase 2 part of the ASTRUM-015 study (serplulimab group, n=55; placebo group, n=57). Among these patients, 90 out of the 94 (95.7%) with available MSI status were MSS. As of June 1, 2023 (data cutoff), the median follow-up duration was 17.7 months. Median progression-free survival (PFS) as assessed by the independent radiology review committee (IRRC) per response evaluation criteria in solid tumours (RECIST) v1.1 was 17.2 months (95% confidence interval [CI] 10.3-not evaluable) in the serplulimab group and 10.7 months (95% CI 8.1-16.6) in the placebo group (stratified hazard ratio [HR] 0.60; 95% CI 0.31-1.14). Median PFS was numerically longer with serplulimab plus bevacizumab and XELOX treatment in the MSS cohort (n = 90); IRRC-assessed median PFS per RECIST v1.1 was 17.2 months (95% CI 9.8-NE) in the serplulimab group and 10.1 months (95% CI 8.1-16.6) in the placebo group (unstratified HR, 0.58; 95% CI 0.30-1.14). Although the median overall survival (OS) was not reached in either group, a trend of a potential benefit was observed with serplulimab treatment (stratified HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.41 to 1.45; P=0.409). The safety profiles of combining serplulimab and HLX04 (bevacizumab, trade name in China: HANBEITAI) in this study were consistent with that of the individual drugs; no new safety signals arose due to the combination in this study.
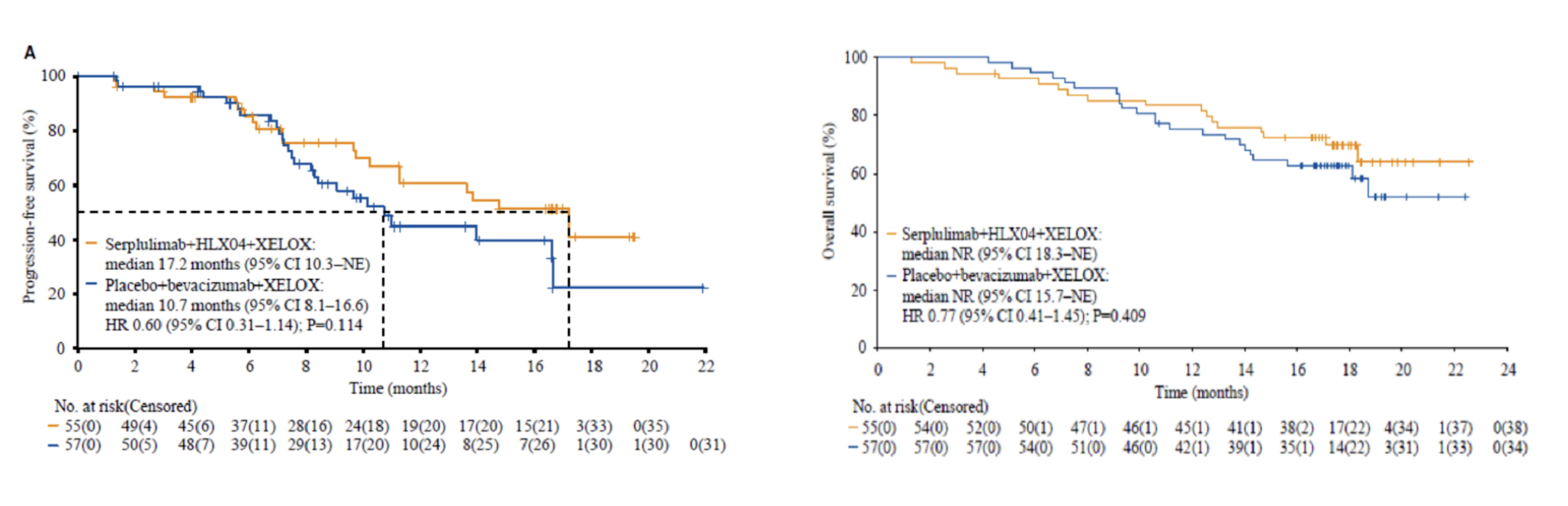
In conclusion, the addition of serplulimab to bevacizumab and chemotherapy conferred a numerically longer median progression-free survival, along with a manageable safety profile for mCRC patients as a whole, and those with MSS mCRC. These results support serplulimab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy as a promising first-line treatment option for mCRC that warrants further investigation. With the accelerated progress of the Phase 3 stage of ASTRUM-015, HANSIZHUANG (serplulimab) is expected to become the world's first anti-PD-1 mAb for previously untreated mCRC and fill the clinical gap in first-line immunotherapy in these patients.
Moving forward, Henlius will actively improve efficiency through innovations, with a particular focus on addressing the unmet medical needs so as to provide more high-quality and affordable therapies for patients worldwide.
【Reference】
[1] Diaz, L. A., Jr. et al. Lancet Oncol 23, 659-670 (2022).
[2] Lenz, H. J. et al. J Clin Oncol 40, 161-170 (2022).
[3] Overman MJ, Kopetz S, McDermott RS, et al. Nivolumab ± ipilimumab in treatment (tx) of patients (pts) with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) with and without high microsatellite instability (MSI-H): CheckMate-142 interim results (abstract). J Clin Oncol 34, 2016 (suppl; abstr 3501).
[4] Overman MJ, Lonardi S, Wong KYM, et al. Durable Clinical Benefit with Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in DNA Mismatch Repair-Deficient/Microsatellite Instability-High Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J Clin Oncol 2018; 36:773.
About Med
Med is a flagship medical journal published monthly by Cell Press. The mission is to advance clinical research and practice by providing a communication forum for the publication of clinical trial results, innovative observations from longitudinal cohorts, and pioneering discoveries about disease mechanisms.
