Shanghai, China, June 4, 2024 –Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc. (2696.HK) announced that the updated results of the company’s self-developed innovative anti-PD-1 mAb, HANSIZHUANG (serplulimab) were released by 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting. These include the pivotal phase 3 clinical study (ASTRUM-005) of serplulimab for the first-line treatment of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) led by Professor Ying Cheng from Jilin Cancer Hospital, and the phase 2/3 study (ASTRUM-015) of serplulimab in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) led by Professor Rui-Hua Xu from Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Guangdong Provincial Clinical Research Center for Cancer; both were released as poster presentations at the meeting.
HANSIZHUANG is the world's first anti-PD-1 mAb approved for the first-line treatment of SCLC. Up to date, it has been approved by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) for the treatment of MSI-H solid tumours, squamous non-small cell lung cancer (sqNSCLC), ES-SCLC, and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The marketing applications of the first-line treatment for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (nsNSCLC) and ES-SCLC are under review by the NMPA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), respectively. Henlius actively promotes HANSIZHUANG in conjunction with in-house products of the company such as tumour-specific target, angiogenesis target, immunotherapeutic target, etc. and chemotherapy drugs to conduct immune-based combination therapies. Underpinned by the patient-centric strategy, Henlius has carried out a differentiated and multi-dimensional layout in the field of gastrointestinal cancer and lung cancer, covering a wide variety of indications, such as lung cancer, ESCC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and gastric cancer, etc. To date, more than 3,900 subjects have been enrolled worldwide for HANSIZHUANG clinical trials.
Lung cancer is one of the most common malignancies around the world. SCLC is the most aggressive subtype of lung cancer, accounting for around 15% of all lung cancer cases[1]. The SCLC breaks down into limited stage small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC) and ES-SCLC. The approvals of HANSIZHUANG for the treatment of ES-SCLC in China and Indonesia were primarily based on ASTRUM-005. The results of ASTRUM-005 were first presented at 2022 ASCO, and published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA). Thereafter, the updated results of ASTRUM-005 were released at the 2022 European Society for Medical Oncology Asia (ESMO Asia) Congress.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common cancers globally. According to the latest report by National Cancer Center (NCC) of China, the incidence and mortality of CRC in China ranked 2nd and 4th among all cancers with 517,000 new cases and 240,000 deaths in 2022[2]. Based on the standard of care for mCRC, Henlius is continuing to explore immuno-oncology therapy for mCRC through the ASTRUM-015 study with the goal of delivering more effective treatment for a broader population of patients. The results of ASTRUM-015 were first presented at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium (ASCO GI).
The updated data of the studies released at 2024 ASCO Annual Meeting are as follows:
ASTRUM-005
Title
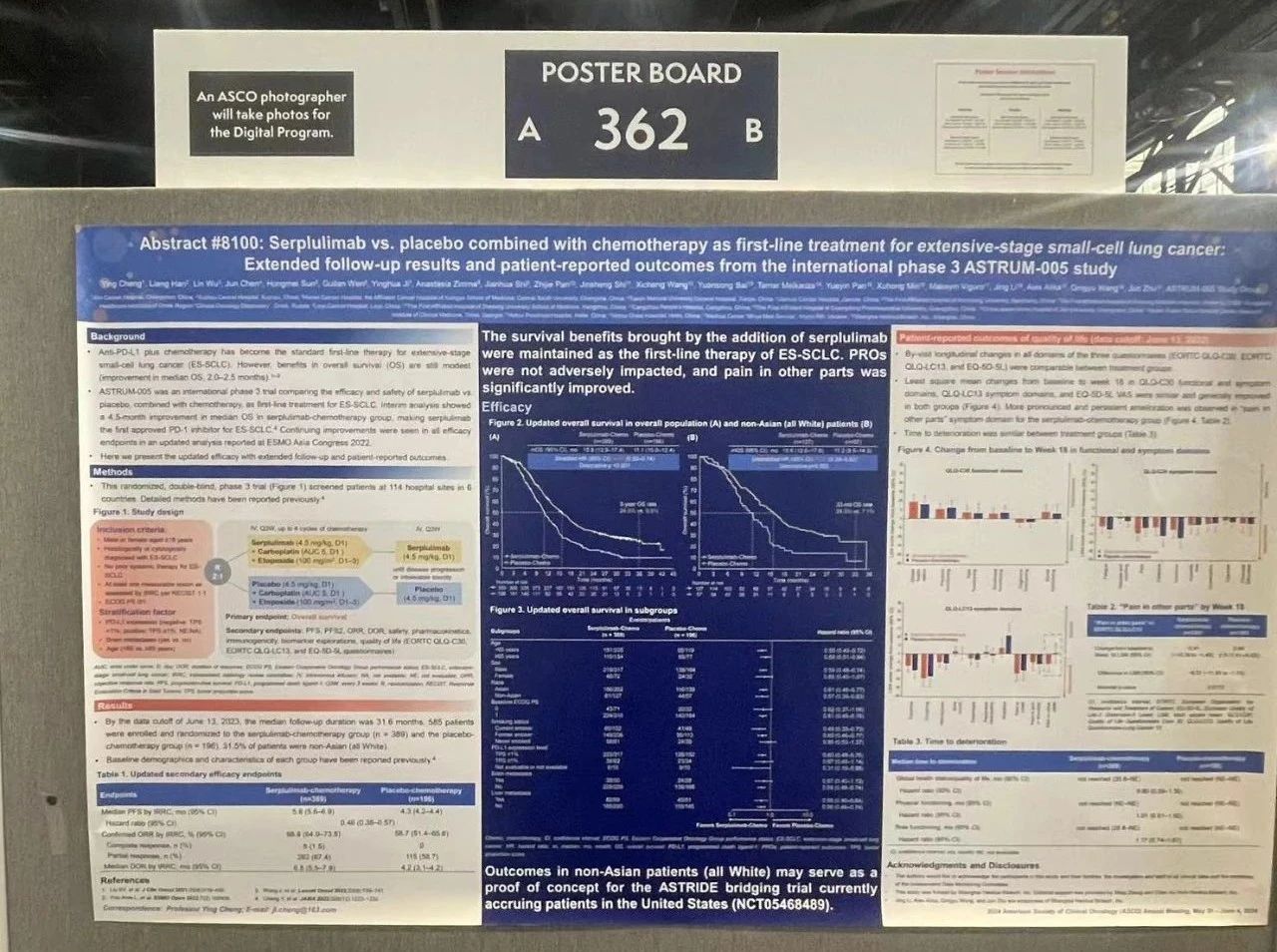
Serplulimab vs. placebo combined with chemotherapy as first-line treatment for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Extended follow-up results and patient-reported outcomes from the international phase 3 ASTRUM-005 study
Study design
ASTRUM-005 is a randomized, double-blind, phase 3 trial comparing efficacy and safety of serplulimab (a novel anti-PD-1 antibody) plus chemotherapy (chemo) vs. placebo plus chemo as first-line therapy for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). 585 patients with ES-SCLC who had not received prior systemic therapy were randomized 2:1 (serplulimab arm, n = 389; placebo arm, n = 196) to receive serplulimab 4.5 mg/kg or placebo intravenously every 3 weeks. All patients received up to 4 cycles of intravenous carboplatin and etoposide every 3 weeks. Stratification factors were PD-L1 expression level, brain metastases, and age. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS). Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) were assessed using EORTC QLQ-C30, EORTC QLQ-LC13, and EQ-5D-5L questionnaires.
Results
By the data cutoff of June 13, 2023, 267 (68.6%) patients in the serplulimab arm and 160 (81.6%) in the placebo arm had died. With an extended follow-up duration of 31.6 months, median OS was markedly longer in the serplulimab arm than that in the placebo arm (15.8 vs.11.1 months; stratified HR 0.61, 95% CI 0.50–0.74). Subgroup analysis by race showed similar trends of a prolonged median OS in Asians (unstratified HR 0.61, 95% CI 0.48–0.77) and non-Asians (all were White; unstratified HR 0.57, 95% CI 0.39–0.83). Estimated OS rate at 3 years was 24.6% (95% CI 19.5–30.1) and 9.8% (95% CI 5.6–15.4) in the respective arms. By-visit longitudinal changes in all domains of the 3 questionnaires were comparable between arms. Least square mean (LSM) changes from baseline to week 18 in QLQ-C30 functional and symptom domains, QLQ-LC13 symptom domains, and EQ-5D-5L VAS were similar and generally improved in both arms, with more pronounced and persistent amelioration in “pain in other parts” symptom domain for the serplulimab arm (difference in LSM change, −6.37 [95% CI −11.59 to −1.15], p = 0.0170). Time to deterioration was similar between arms: median, not reached (NR) vs. NR for global health status/quality of life (HR 0.90, 95% CI 0.59–1.39), physical functioning (HR 1.01, 95% CI 0.61–1.65), and role functioning (HR 1.17, 95% CI 0.74–1.87).
Conclusion
With extended follow-up, the survival benefits brought by the addition of serplulimab were maintained in the first-line therapy of ES-SCLC. PROs were not adversely impacted, and pain in other parts was significantly improved. All these results support serplulimab plus chemo as a promising first-line treatment option for ES-SCLC.
ASTRUM-015
Title
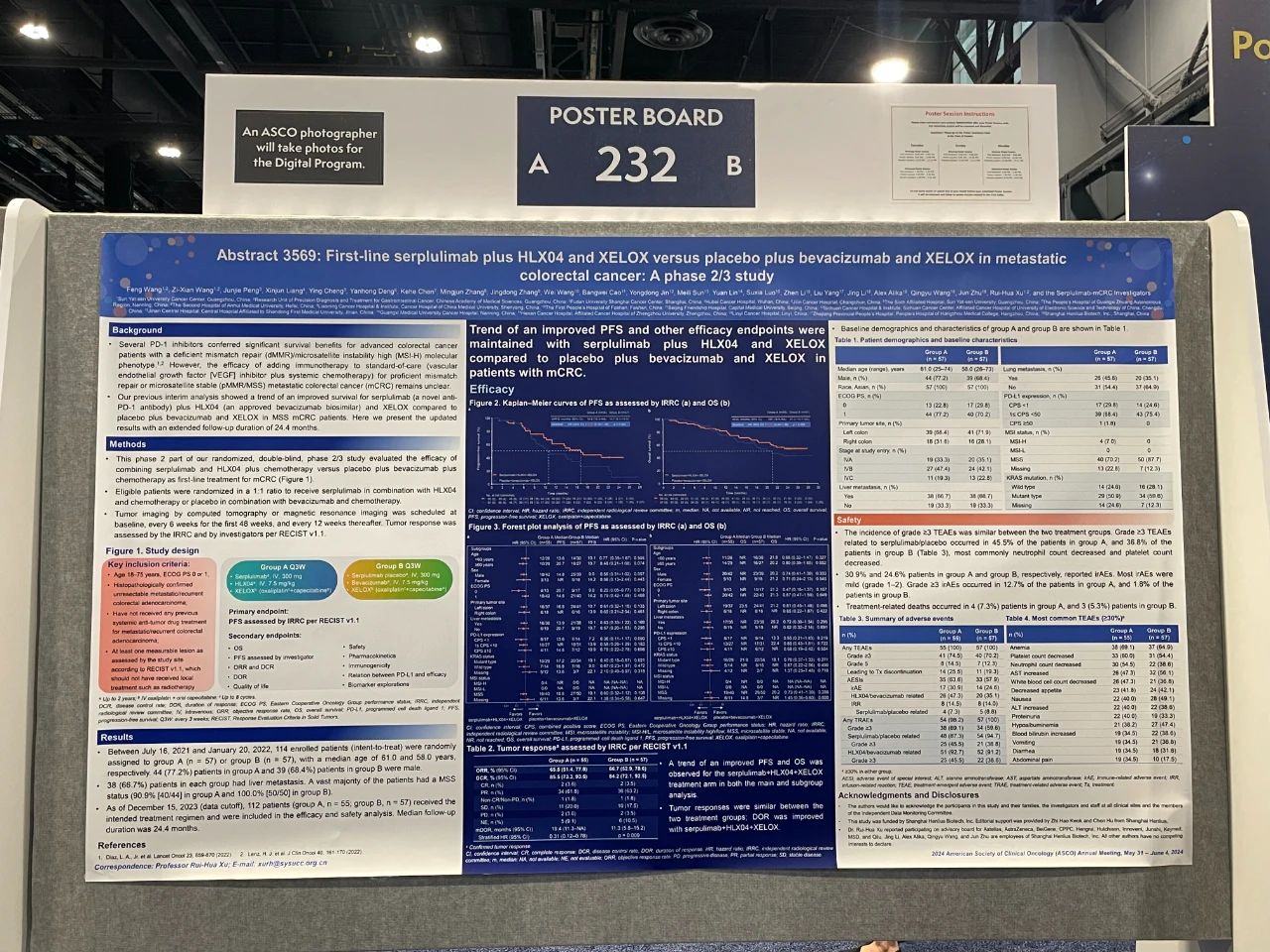
First-line serplulimab plus HLX04 and XELOX versus placebo plus bevacizumab and XELOX in metastatic colorectal cancer: a phase 2/3 study
Study design
This is a randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase 2/3 study comparing the efficacy and safety of serplulimab (a novel anti-PD-1 antibody) plus HLX04 (an approved bevacizumab biosimilar) and XELOX chemotherapy vs. placebo plus bevacizumab and XELOX as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). In the phase 2 part, 114 patients with mCRC and no prior systemic therapy were randomized 1:1 (serplulimab arm, n = 57; placebo arm, n = 57) to receive intravenous (IV) serplulimab (300 mg) plus HLX04 (7.5 mg/kg) and XELOX (IV oxaliplatin [130 mg/m2] and oral capecitabine [1000 mg/m2]) (group A) or placebo plus bevacizumab and XELOX (group B) once every 3 weeks. Stratification factors were PD-L1 expression level, ECOG PS score, and primary tumor site. The primary endpoint was independent radiological review committee (IRRC)-assessed progression-free survival (PFS) per RECIST 1.1. Secondary endpoints included other efficacy endpoints, safety, pharmacokinetics, biomarker explorations, and quality-of-life assessments.
Results
By the data cutoff of December 15, 2023, with an extended follow-up duration of 24.4 months, the primary endpoint of independent radiology review committee (IRRC)-assessed median progression-free survival (PFS) was improved with serplulimab plus HLX04 and XELOX (n = 55) at 16.8 months compared to placebo plus bevacizumab and XELOX (n = 57) at 10.7 months, with a reduction in risk of disease progression or death by 42% (HR=0.58). A potential PFS benefit was consistently observed for key subgroups including microsatellite stable (MSS) (16.8 vs. 10.1 months, HR = 0.60), KRAS mutant (17.2 vs. 10.1 months, HR = 0.40), and liver metastasis (13.9 vs. 10.1 months, HR = 0.63) patients. A trend of an improved median overall survival was also observed with serplulimab plus HLX04 and XELOX over placebo plus bevacizumab and XELOX in the main (not reached vs. 21.2 months, HR = 0.74), as well as subgroup analysis. Median duration of response was prolonged for the serplulimab arm compared to placebo (19.4 vs. 11.3 months, HR = 0.31).
Conclusion
With an extended follow-up duration, improved survival benefits demonstrated with the addition of serplulimab were maintained in the first-line treatment of mCRC, alongside a manageable safety profile. These results support serplulimab plus HLX04 and XELOX as a promising first-line treatment option for mCRC that warrants further investigation.
ASTRUM-005R

Title
Real-world first-line serplulimab-based immunochemotherapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: The Multicenter ASTRUM-005R study
Conclusion
This cohort study reports the real-world survival outcomes of first-line serplulimab-based immunochemotherapy and provides valuable insights in a clinical setting. The study complements the ASTRUM-005 study, offering further evidence in ES-SCLC.
A retrospective study in LS-SCLC

Title
Neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy in patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer: A retrospective study
Conclusion
Neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibitors combined with chemotherapy demonstrated promising efficacy and feasibility, and are a potential strategy for the management of LS-SCLC. Further prospective clinical trials are necessary to clearly define the benefit of neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy and optimize LS-SCLC treatment.
A randomised controlled, open-label, phase 2 trial in NSCLC

Title
Induction therapy with PD-1 antibody combined with platinum-based doublet chemotherapy for locally-advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A randomised controlled, open-label, phase 2 trial
Conclusion
Induction therapy with PD-1 antibody (Serplulimab) and chemotherapy could transform half of unresectable stage IIIB-IIIC NSCLC into resectable, and the efficacy and safety were satisfactory.
A phase 2 study in EGJ adenocarcinoma

Title
Neoadjuvant serplulimab in combination with concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced, resectable esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma
Conclusion
Initial benefits were demonstrated when using Serplulimab with concurrent chemoradiotherapy for the treatment of locally advanced, resectable EGJ adenocarcinoma patients. The efficacy and safety of Serplulimab with chemoradiotherapy will be further investigated in this trial later.
A real-world retrospective study in gastric cancer

Title
Effectiveness and safety analysis of serplulimab-based regimens in patients with
HER2-negative advanced gastric cancer from a real-world retrospective study
Conclusion
The real-world data analysis shows that serplulimab-based flexibly combination according to patient status, achieving tumor control in diverse pts while ensuring drug safety. We successfully validated the effectiveness and safety of chemo-immunotherapy strategy in real-world practice.
A study in first-line treatment of NEC

Title
Efficacy and safety of surufatinib combined with EP regimen and serplulimab in firstline treatment of NEC
Conclusion
Surufatinib combined with the EP regimen and serplulimab for NEC as first-line treatment showed notable efficacy and safety. The study established a phase II recommended surufatinib dose of 250mg, alongside immunotherapy and chemotherapy.
A real-world study in EC

Title
Effectiveness and safety of first-line serplulimab in patients with metastatic/locally
advanced esophageal carcinoma (EC): A real-world study.
Conclusion
First-line serplulimab combined with chemotherapy demonstrated promising effectiveness and favorable safety profile in patients with metastatic/locally advanced EC, especially in ESCC. The current real-world evidence indicates that serplulimab combined with chemotherapy could provide survival benefit for patients with advanced first-line EC.
【Reference】
[2] B Han et al. J Natl Cancer Cent, 4(1), 47-53 (2024).
[1] Eskandar A, Ahmed A, Daughtey M, et al. Racial and sex differences in presentation and outcomes of small cell lung cancer in the United States: 1973 to 2010[J].Chest, 2015,147(4): e164-e165.
About HANSIZHUANG
HANSIZHUANG (recombinant humanized anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody injection, generic name: serplulimab injection) is the first anti-PD-1 mAb for the first-line treatment of SCLC and has been approved in China and Indonesia. Up to date, 4 indications are approved for marketing, 2 marketing applications are under review in China and the EU, and more than 10 clinical trials are ongoing across the world.
HANSIZHUANG was approved in China in March 2022 and has been approved by the National Medicinal Products Administration (NMPA) for the treatment of MSI-H solid tumours, squamous non-small cell lung cancer (sqNSCLC), extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC), and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The marketing applications of the first-line treatment for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (nsNSCLC) and ES-SCLC are under review by the NMPA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), respectively. Focus on lung and gastrointestinal cancer, the synergy of HANSIZHUANG with in-house products of the company and innovative therapies are being actively promoted. The company has initiated more than 10 clinical trials on immuno-oncology combination therapies in a wide variety of indications with more than 3,900 subjects enrolled in China, the U.S., Turkey, Poland, Georgia and other countries and regions. The results of 4 pivotal trials of HANSIZHUANG were published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), Nature Medicine, Cancer Cell, and the British Journal of Cancer, respectively. Furthermore, HANSIZHUANG was respectively recommended by the CSCO Guidelines for Small Cell Lung Cancer, the CSCO Guidelines for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, the CSCO Guidelines for Esophageal Cancer, the CSCO Guidelines for Colorectal Cancer, the CSCO Clinical Practice Guidelines on Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor, the China Guidelines for Radiotherapy of Esophageal Cancer, and other definitive guides, providing valuable references for clinical diagnosis and treatment of tumours. On the other hand, serplulimab was granted orphan drug designations by the U.S. FDA and the EC for the treatment of SCLC, and its bridging head-to-head trial in the United States to compare HANSIZHUANG to standard of care atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1 mAb) for the first-line treatment of ES-SCLC is well under way.
